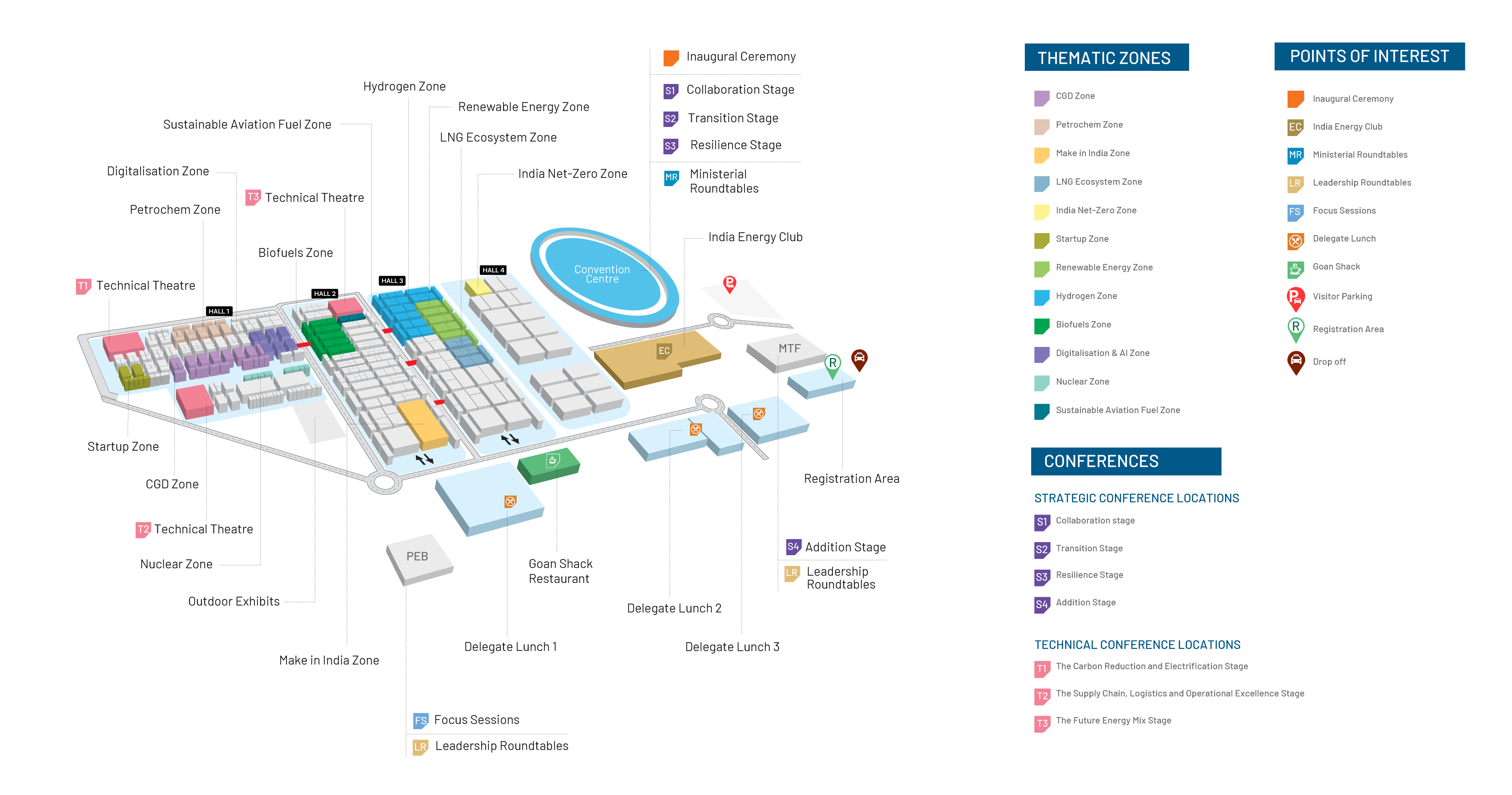
Advanced biofuels—particularly Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) and Second-Generation (2G) Ethanol—are at the forefront of India’s clean energy transition. Derived from non-food, waste-based, and renewable feedstocks such as agricultural residues, used cooking oil, lignocellulosic biomass, and MSW-derived lipids, advanced biofuels offer a high-impact pathway for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors while strengthening energy security and fostering rural development.
SAF is globally recognized as the most scalable near-term solution for aviation decarbonization. As countries commit to CORSIA and long-term net-zero targets, SAF demand is set to rise sharply. With its abundant biomass resources, strong refining capabilities, and rapidly expanding aviation market, India is uniquely positioned to emerge as a global leader in SAF production and adoption.
Parallelly, 2G ethanol plays a vital role in India’s energy diversification strategy by converting crop residues into clean fuel, reducing stubble burning, enhancing rural incomes, and supporting the national ethanol blending program. The development of 2G biorefineries also creates synergies with future SAF pathways, enabling a more integrated and resilient bioenergy ecosystem.
Together, SAF and 2G biofuels represent India’s opportunity to build a world-class bioeconomy—one that delivers climate benefits, drives industrial innovation, and supports India’s long-term Net Zero 2070 vision.